What causes heartburn, and how to treat it
What you need to know:
- Heartburn, a symptom of acid reflux, is easily treated with over-the-counter medications.
- It occurs after eating heavy meals and meals or drinks rich in fats or acid.
- Pregnant women also often suffer heartburn.
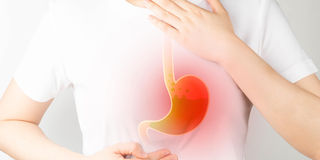
Heartburn is a symptom of acid reflux, which occurs when stomach acid flows back into the oesophagus. Heartburn is usually felt as a burning sensation in the chest, behind the breastbone. Acid reflux can also cause other symptoms such as a sour taste in the mouth, difficulty swallowing, and regurgitation.
It often occurs after eating a large meal, acidic foods, or beverages such as coffee or soda. Heartburn can also be triggered by lying down or bending over, as this position allows stomach acid to flow more easily back into the oesophagus.
Heartburn usually lasts for a few minutes and can be relieved by home remedies. However, in some cases, it can last for several hours and may require more aggressive treatment.
Heartburn that occurs more than twice a week is called gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). GERD can lead to other medical problems, such as Barrett's oesophagus and oesophageal cancer.
Symptoms associated with heartburn
The most common heartburn symptoms are a burning sensation in the chest or throat and a sour taste in the mouth. Heartburn can also cause a feeling of heaviness or pressure in the chest and may be accompanied by nausea or vomiting.
Causes and risk factors
Heartburn is caused by stomach acid flowing back up into the oesophagus. The lower oesophageal sphincter is a muscle that separates the oesophagus from the stomach. This muscle relaxes to allow food and liquid to pass into the stomach, then contracts to prevent acidic stomach contents from flowing back into the oesophagus.
Certain lifestyle choices can increase the risk of heartburn, such as eating large meals, lying down or bending over after eating, and consuming certain foods and beverages. These include fatty or fried foods, spicy foods, citrus fruits, tomatoes, chocolate, mints, coffee, or soda.
In addition, pregnancy and obesity can also increase the risk of heartburn.
Diagnosis
Heartburn is usually diagnosed based on symptoms. A physical examination and medical history may be needed to diagnose heartburn. In some cases, additional tests may be ordered to rule out other conditions such as GERD or peptic ulcer disease. These tests may include an endoscopy, in which a small camera is used to examine the inside of the oesophagus.
An X-ray or CT scan may be recommended to observe the stomach and oesophagus condition.
Treatment
Heartburn can usually be treated at home with over-the-counter medications such as antacids, H-blockers, and proton pump inhibitors. These medications are available in both prescription and over-the-counter strength.
Lifestyle changes such as weight loss and diet change play an important part in resolving heartburn.
Difference between heartburn and acid reflux
Heartburn is a symptom of acid reflux, but it is not the same thing. Acid reflux is a condition in which stomach acid flows back into the oesophagus.
Difference between acid reflux and GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a more severe form of acid reflux. GERD can lead to serious medical problems such as oesophageal cancer. This requires urgent medical attention. In some cases, GERD can also lead to respiratory problems. The acidic stomach contents that flow back into the oesophagus can irritate the throat and lungs, leading to coughing, wheezing, and even asthma.
Heartburn complications
If left untreated, acid reflux can lead to complications such as esophagitis, Barrett's oesophagus, and even cancer of the oesophagus. In addition, acid reflux can cause tooth decay, as the acids wear away at the enamel of the teeth.
Heartburn prevention
You can do several things to prevent heartburn, such as avoiding trigger foods and beverages, eating smaller meals, and avoiding lying down or bending over after eating. Additionally, losing weight if you are overweight and quitting smoking can help prevent heartburn.
Various home remedies may help prevent or relieve heartburn symptoms, such as chewing gum, staying upright, or taking ginger. However, it is important to talk to your doctor before trying any home remedies, as some may interact with medications you are taking or have other risks.
When to see a doctor
You should see your doctor if you experience heartburn more than once a week. Additionally, consult your doctor if you have difficulty swallowing, nausea, vomiting, or weight loss. These may be signs of more severe conditions. If you experience blood in the vomit, pain in the jaws, neck, and arm, seek help.
Conclusion
Heartburn is a symptom of acid reflux that can affect one's daily activities. It varies in severity and time.
Heartburn can usually be treated at home with over-the-counter medications and home remedies, but some cases may require prescription medications or surgery.




