Cataracts: When your eye's natural lens becomes cloudy
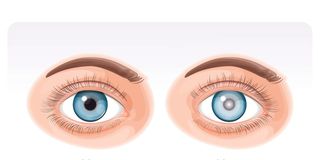
A cataract refers to clouding of part of the whole lens of the eye, which is usually clear.
What you need to know:
- The risk of developing cataracts is higher if there’s a positive family history of cataracts, or if you have some illnesses such as diabetes, or due to long terms use of steroids.
- Excessive alcohol consumption, smoking and prolonged exposure to the sun also increase the risk of developing cataracts.
Dear doctor,
I had an eye check-up last week and was told that I have an early cataract. How does it come about, and what are the treatment options?
Robin
Dear Robin,
A cataract refers to clouding of part of the whole lens of the eye, which is usually clear. The eyes have a lens which focuses the rays of light on the back of the eye (retina) so that the images seen can be sharp and clear. A cataract forms when the fibres and proteins in the lens break down and clump together.
The most common cause of cataracts is age as the lens becomes less flexible, thicker and cloudy. A cataract may also form as a result of an eye injury, or following surgery for another eye problem (such as glaucoma) or following radiotherapy.
The risk of developing cataracts is higher if there’s a positive family history of cataracts, or if you have some illnesses such as diabetes, or due to long terms use of steroids. Excessive alcohol consumption, smoking and prolonged exposure to the sun also increase the risk of developing cataracts. Cataracts usually develop slowly over time and may affect one or both eyes, though usually when they affect both eyes, the rate of cataract development may be different. Initially, there may be no symptoms and then as the cataract worsens, there may be blurring of vision; colours look faded; poor night vision; double vision; seeing haloes around lights and having challenges seeing when the light is dim or too bright. You will also notice that you need to keep changing the prescription of your eye glasses or contact lenses.
A cataract is diagnosed through a dilated eye exam, which is usually part of an eye examination. The dilated exam should be carried out every one to two years for all persons over the age of 60.
For an early cataract, the management is to use bright light at home and at work, use anti-glare glasses, regularly update eyeglass prescriptions and/or using a magnifying glass for reading. For severe symptoms that interfere with daily activities, cataract surgery is done where the cloudy lens is removed and replaced with a clear artificial lens.
Dear doctor,
My wife is eight months pregnant. My concern is that she has had several UTIs in the course of the pregnancy. Is there a reason for this? Are the UTIs likely to affect the baby and is there a way to prevent that? Patrick
Dear Patrick,
An UTI is an infection affecting any part of the urinary system, from the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra. Women are more likely to get UTIs because of having a shorter urethra (the tube carrying urine from the bladder to the outside). During pregnancy, the risk of developing a UTI increases due to the hormonal changes and also because the urine is less acidic and has more sugars and proteins. In addition, the growing uterus presses on the urinary bladder and the uterus, which can cause reflux and stagnation. The distended belly also makes hygiene a challenge. The risks of getting a UTI also increase if the mother has an illness that lowers the immunity, bladder problems or if there is tobacco use.
The potential complications of having a UTI in pregnancy include infection spread to the kidneys and to the rest of the body, premature delivery, having a baby with low birth weight and spread of infection to the baby. Symptoms of UTI include having a burning sensation when passing urine, passing urine frequently, feeling an urgent need to pass urine, having blood/pus in urine and low abdominal pain. There may also be fever, nausea and back pain. Sometimes pregnant women may have a UTI with no accompanying symptoms.
Urine analysis should be done at every clinic visit during antenatal care, and the individual should be reviewed any time they have any UTI symptoms. UTIs are usually treated with oral antibiotics, with kidney or widespread infections requiring admission for treatment. The doctor may also advise on taking prophylactic antibiotics to prevent UTI if the infections have been recurrent. Measures to reduce the risk of getting a UTI include taking adequate amounts of water; taking cranberry juice; passing urine when the urge arises or every two to three hours; maintaining good genital hygiene; passing urine before and after sexual intercourse; and screening for UTI during antenatal visits.
Dear doctor,
I have had nausea almost daily for the past three weeks, and I do not have any abdominal pain. What could be causing it and how do I get rid of it?
Mutiso
Dear Mutiso,
Nausea refers to the urge to vomit and it is usually accompanied by stomach discomfort, though not always. There are many possible causes of nausea including smells, specific foods, stomach infection, hyperacidity, reflux and having peptic ulcers. You can also develop nausea if you overeat or take excess amounts of alcohol, or when you experience emotional stress.
Other illnesses can also cause nausea such as flu, migraine headaches, problems in the brain, or problems with any of the abdominal organs such as liver, kidney, gall bladder, pancreas and intestines
To be able to identify the underlying cause of the nausea, it is advisable for you to be reviewed by a doctor, and any necessary tests will be done. The treatment will be tailored to the diagnosis. There are also medications for nausea.
To prevent nausea, eat slowly and stay upright thereafter; take small frequent meals; take adequate amounts of water in between meals (not during meals); avoid intense physical activity after a heavy meal; and avoid spicy and high-fat foods, or any other foods that worsen the nausea. Also avoid strong smells. When nauseated, rest with your upper body upright and take small sips of water.